JAPAN

/1/
Definitions of
non-road mobile
machinery
The term non-road vehicles as used in the definitions provided from Article 2 of Chapter 1 in Law No. 51 of May 25, 2005 of the Japanese Ministry of the Environment refers to those motor vehicles, as defined in Article 2, Paragraph 2 of the Road Vehicles Act (Law No. 185 of 1951) except for equipment for towing other vehicles and other equipment specified by order of the Cabinet of Japan (2005):
- Large-sized special motor vehicles and special small-sized special motor vehicles provided for in Article 3 of the Road Vehicles Act; and
- Motor vehicles that fall under the category of construction machinery provided for in Article 2 of the Construction Machinery Hypothecation Act (Act No.97 of 1954) (except those enumerated in the preceding item) and other motor vehicles which have special structures and which shall be specified by Japanese Cabinet order.
The term non-road engine as used in this Act means an engine which is installed in a non-road vehicle and a device which is installed in a unibody therewith which is specified by order of the competent ministry (Act on Regulations for Emissions from Non-Road Vehicles (Act No. 51 of May 25, 2005).
The term emissions from non-road vehicles as used in this Act refers to substances such as carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons and lead generated by the use of non-road special motor vehicles which may possibly cause damage to the human health or living environments and which shall be specified by the Japanese Cabinet order. (Act on Regulations for Emissions from Non-Road Vehicles (Act No. 51 of May 25, 2005).
Special motor vehicles can be specified as motor vehicles other than ordinary sized motor vehicles, small-sized motor vehicles and mini-sized motor vehicles and other than passenger vehicles, trucks or buses.
Emission standards for so-called special motor vehicles (all intended for off-road operation) apply to vehicles with engines rated between 19-560 kW categorised into two types:
- Special motor vehicles: “self-propelled non-road vehicles as well as machinery that are registered for operation on public roads (fitted with license plates)” (Dieselnet, 2016). “This is a type of motor vehicle that could be operated on public roads such as an agricultural tractor or a forklift” (Act on Regulations for Emissions from Non-Road Vehicles (Act No. 51 of May 25, 2005). Special motor vehicles can be specified as motor vehicles other than ordinary sized motor vehicles, small-sized motor vehicles and mini-sized motor vehicles and other than passenger vehicles, trucks or buses. These vehicles have registration plates and could possibly be used on the road even though this is not their place of operation (LEMA, 2019).
- Non-road special motor vehicles: “self-propelled and non-registered non-road vehicles and machinery” (Dieselnet, 2016). “These are a type of motor vehicle that never travels on a public road such as a bulldozer or a construction crane tower” (Act on Regulations for Emissions from Non-Road Vehicles (Act No. 51 of May 25, 2005). Non-road special motor vehicles are those mobile machines for non-road operation that are propelled on the ground by the engine installed in the vehicles just like special-purpose vehicles, but differ from these in that non-road special motor vehicles never travel on public roads, do not have license plates and are used in other non-road locations (LEMA, 2019).
“Engines installed in either special motor vehicles or non-road special motor vehicles are intended to use for propelling its vehicles, as well as for promoting work on construction sites where they are used”. (LEMA, 2019).
For special motor vehicles and non-road special motor vehicles with an engine installed capacity between 19 and 560 kW, emission limits have been specified under the provision of the Air Pollution Control Act (Act No. 97 of 1968) and legislative control is to be performed by the Non-road Vehicle Emission Regulation Act (Act No. 51 of 25 May 2005). (Dieselnet, 2016).

/2/
Main regulatory
instruments for NRMM
emissions reduction
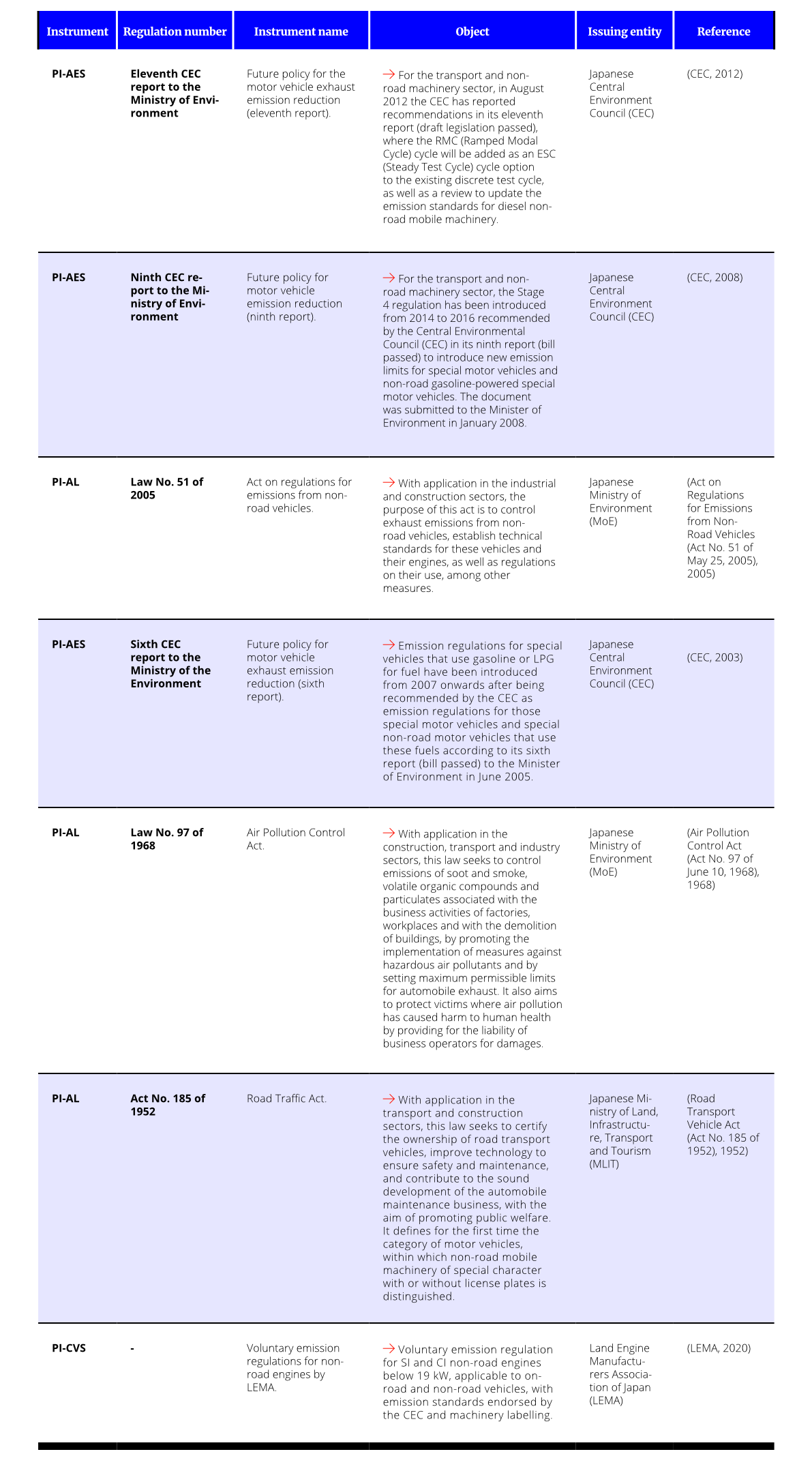
A compilation of different types of instruments identified in Japan for the control of air pollution generated by NRMM is presented in Table 1.
Tabla 1
Regulatory framework and identification of NRMM emission reduction tools – Japan.
Source: self made.
From axis #3 to axis #9
No information for Japan
Consultation documents (downloadable)







